Unlock the potential of Enterprise Agile Transformation. Embrace Agile values for adaptability and innovation, driving success in the business world.
In today’s rapidly evolving business landscape, numerous large organizations are confronted with the need to embrace agile transformation, a highly challenging task. For those accustomed to traditional management approaches, venturing on the path to agile transformation involves a major shift in organizational culture. This includes changes in workforce attitudes, core company values, and overall mindset.
The necessity to adapt swiftly and the relentless pressure to keep up with changes have made organizations actively pursue greater agility. In fact, the significance of this shift is evident in executive circles, with a staggering 90% of them acknowledging the importance of agile transformation, and 60% rating it as a top priority according to a Deloitte survey.
This blog will explore the ways to achieve a thriving agile transformation within your organization. We’ll also delve into practical strategies for driving and managing this process while highlighting the role of communication in fostering and empowering the adoption of a traditional to agile mindset among the workforce.
Let’s dig in!
What is enterprise Agile transformation?
Enterprise Agile transformation is a comprehensive shift in the way organizations conduct business. Rooted in Agile principles, this transformation moves beyond the confines of software development and extends its benefits to the entire enterprise. It represents a strategic approach that aims to enhance collaboration, flexibility, and responsiveness to market dynamics.
By adopting Agile methodologies, companies can streamline processes, improve product quality, and, most importantly, respond to customer needs in real time.
The essence of Agile methodology
At its core, Agile is a set of principles designed to promote iterative development, continuous feedback, and customer-centricity. Agile methodologies, such as Scrum and Kanban, replace rigid long-term planning with shorter development cycles known as sprints. These sprints enable cross-functional teams to collaborate closely, identify potential bottlenecks, and make necessary adjustments swiftly.
The iterative nature of Agile allows for the delivery of smaller, incremental improvements, empowering businesses to gather feedback early in the process. This approach reduces the risk of investing time and resources into features that may not resonate with the end users.
Benefits of Agile transformation in various industries
- Information Technology (IT) industry: Agile methodologies, such as Scrum and Kanban, have been widely adopted in the IT sector. By embracing Agile practices, software development teams can deliver incremental updates and improvements regularly, ensuring faster time-to-market.
Agile fosters better collaboration between cross-functional teams, enabling them to respond swiftly to changing project requirements. Moreover, continuous feedback loops enhance the quality of software products, resulting in higher customer satisfaction and reduced development costs.
- Manufacturing industry: In manufacturing, Agile principles drive operational efficiency by streamlining processes and reducing waste. Manufacturers can quickly adapt to market demands, introducing new products or modifications to existing ones faster.
Agile practices facilitate seamless coordination between different production stages, reducing lead times and inventory costs. It also promotes a customer-centric approach, allowing manufacturers to align production with changing consumer preferences and market trends.
- Marketing and advertising: The dynamic nature of the marketing and advertising industry demands flexibility and responsiveness to emerging trends. Agile transformation empowers marketing teams to respond rapidly to market shifts, adjust campaigns in real-time, and optimize strategies for better results.
Regular feedback loops and data-driven decision-making enhance campaign performance and customer engagement, leading to higher ROI for marketing initiatives.
- Healthcare: The healthcare industry can benefit from Agile transformation by improving patient care and operational efficiency. Agile methodologies, when applied to healthcare settings, can enhance communication among medical teams, leading to better patient outcomes.
By employing Agile practices, healthcare organizations can develop and implement new technologies, medical devices, or treatment methodologies more efficiently, fostering innovation and advancing patient care.
- Education: Agile transformation can revolutionize the education sector by promoting learner-centric approaches. Agile principles encourage educators to adapt teaching methods and content based on individual student needs, improving learning outcomes. Schools and educational institutions can also benefit from Agile project management, ensuring smooth coordination of administrative tasks and curriculum development.
Understanding traditional project management
Project management is the cornerstone of successful endeavors, providing structure and direction to achieve desired outcomes. For many years, traditional project management (PM) methodologies have been the go-to approach for enterprises and companies across various industries. However, with the ever-changing landscape of technology and business, it is crucial to understand the characteristics, challenges, and limitations of traditional project management.
Definition and characteristics of traditional project management
Traditional project management is a linear and sequential approach that follows a well-defined set of phases: initiation, planning, execution, monitoring, and closure. It relies on detailed, upfront planning, where project requirements and objectives are thoroughly documented before any work begins. The focus is on adhering to a predetermined schedule, budget, and scope, with a rigid hierarchical structure.
Characteristics of traditional project management include:
- Fixed scope and timeline: Projects are planned in detail at the beginning, and changes to scope or timeline are discouraged during execution.
- Hierarchical organization: Roles and responsibilities are strictly defined, with decision-making concentrated at the top of the hierarchy.
- Waterfall approach: The project progresses in a linear, step-by-step manner, where each phase must be completed before moving on to the next.
- Emphasis on documentation: Extensive documentation is created to ensure a clear understanding of project requirements and processes.
Common challenges and limitations of traditional approaches
While traditional project management has been widely used in the past, it is not without its challenges and limitations. Some of the key issues include:
- Lack of flexibility: The rigid nature of traditional project management makes it challenging to adapt to unexpected changes, such as shifting priorities or new opportunities.
- Inaccurate initial estimations: Detailed upfront planning may lead to inaccuracies in estimating project costs and timelines, resulting in potential delays and budget overruns.
- Limited stakeholder engagement: Due to the hierarchical structure, lower-level team members may have limited involvement in decision-making, leading to reduced motivation and creativity.
- Risk of scope creep: Changes to project requirements may arise during the development process, leading to scope creep and project drift.
- Delayed feedback loops: Feedback from stakeholders and end-users may only be collected after the project is completed, reducing opportunities for course correction.
Introduction to Agile methodology
In this section, we will explore the core principles of Agile, the Agile Manifesto, and its values, and key Agile frameworks to help businesses make informed choices based on project requirements.
Definition and core principles of Agile
At its essence, Agile is a collaborative and iterative approach to project management that prioritizes customer value and encourages adaptability to change. Agile methodologies emphasize delivering incremental, high-quality results in short cycles called iterations or sprints. This iterative process allows teams to gather feedback early and make adjustments promptly, ultimately leading to better outcomes and a more customer-centric approach.
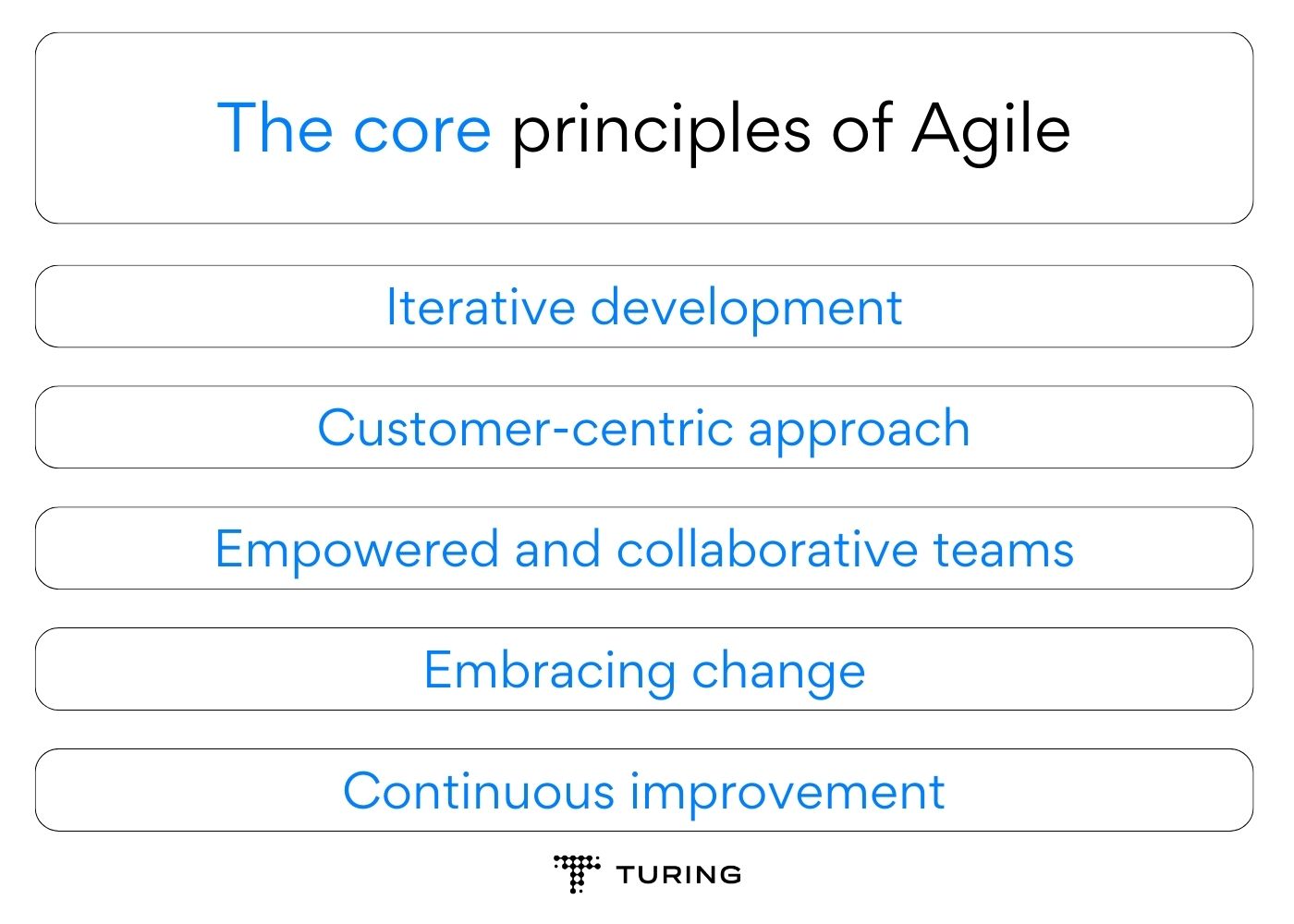
The core principles of Agile include
The core principles of Agile
- Iterative development: Agile emphasizes breaking down projects into smaller, manageable iterations or sprints. Each iteration results in a functional and potentially releasable product increment, allowing for continuous improvement and feedback.
- Customer-centric approach: Customer satisfaction is at the heart of Agile. By involving customers and stakeholders throughout the development process, teams can gain valuable insights, address evolving needs, and ensure that the final product meets or exceeds customer expectations.
- Empowered and collaborative teams: Agile promotes self-organizing, cross-functional teams. Team members have the autonomy to make decisions and collaborate closely, fostering a sense of ownership and shared responsibility for project success.
- Embracing change: Rather than resisting change, Agile embraces it as a natural part of the development process. Teams are encouraged to adapt and respond to changing requirements, market conditions, or customer feedback to maximize value delivery.
- Continuous improvement: Agile encourages a culture of continuous learning and improvement. Teams regularly reflect on their processes, identify areas for improvement, and implement changes to become more efficient and effective.
Agile Manifesto and its values
The Agile Manifesto, formulated in 2001 by a group of software development experts, serves as the guiding philosophy of Agile methodology. It outlines four core values that set the foundation for Agile practices:
- Individuals and interactions over processes and tools: The primary focus should be on the people involved in the project and fostering effective communication and collaboration between team members.
- Working software over comprehensive documentation: The ultimate measure of progress is the delivery of functional software that provides value to the customer.
- Customer collaboration over contract negotiation: Building strong relationships with customers and involving them in the development process ensures that the final product meets their actual needs.
- Responding to change over following a plan: Agile embraces change as a natural part of development, acknowledging that requirements and priorities may evolve throughout the project.
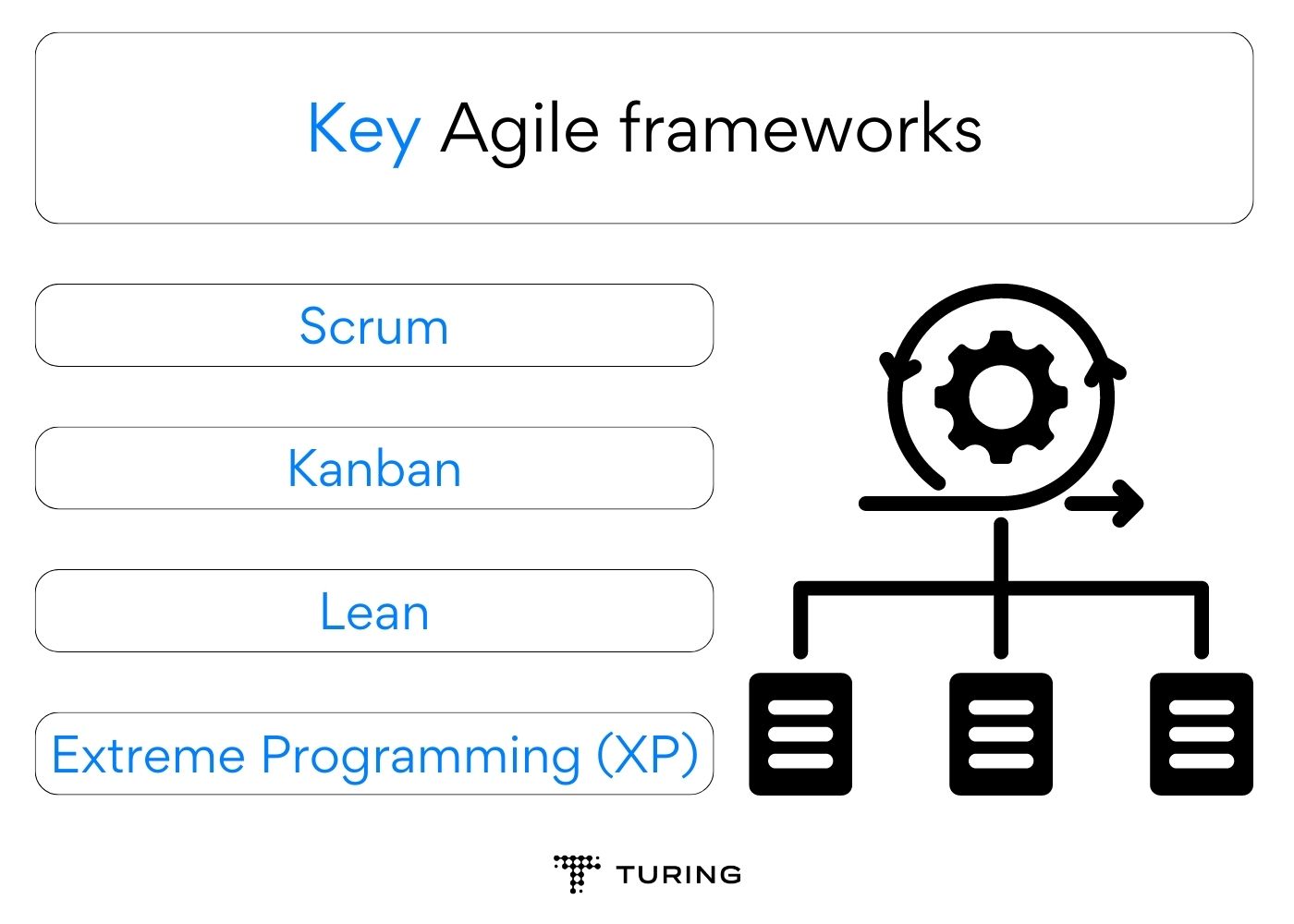
Key Agile frameworks
Key Agile frameworks
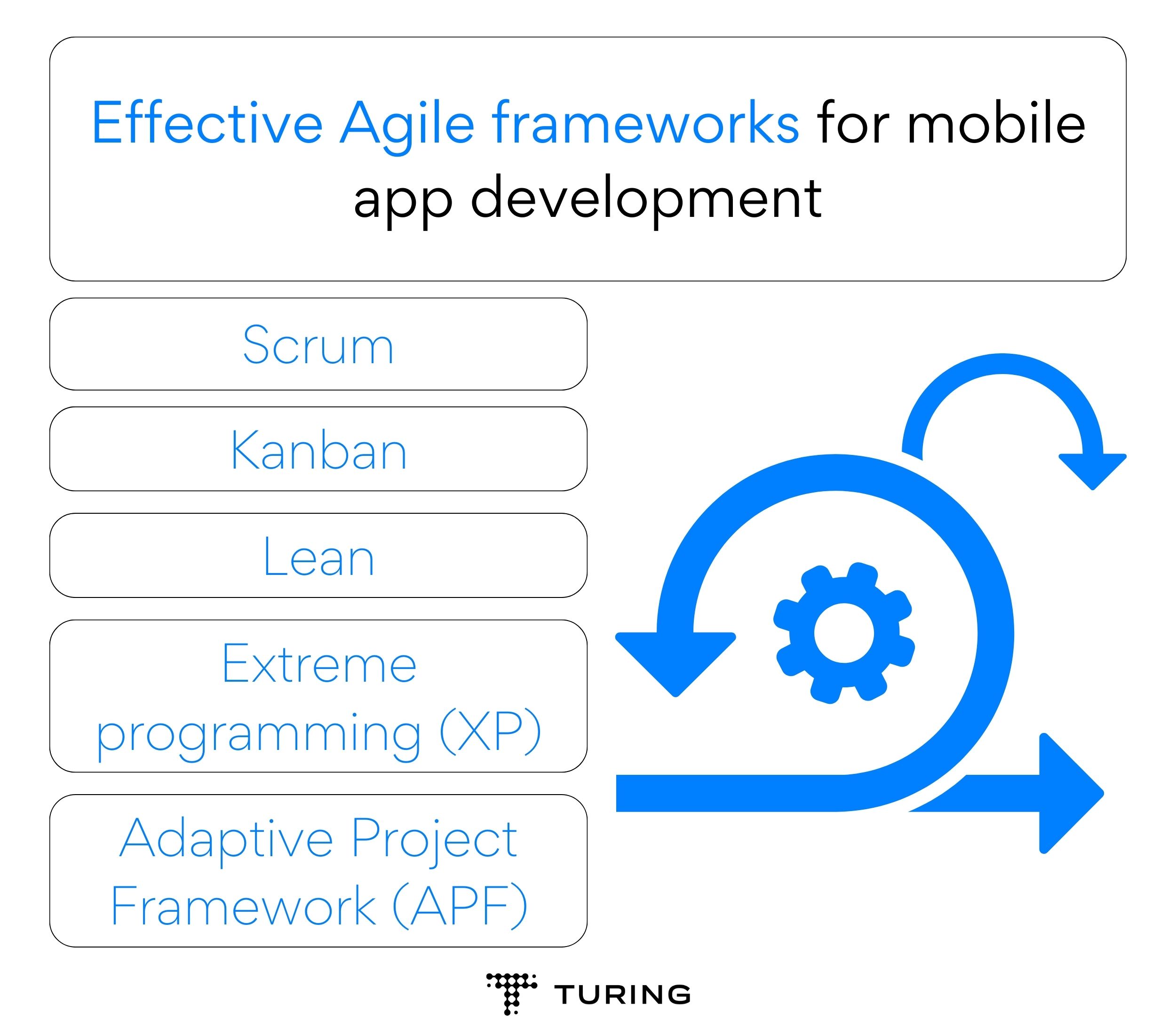
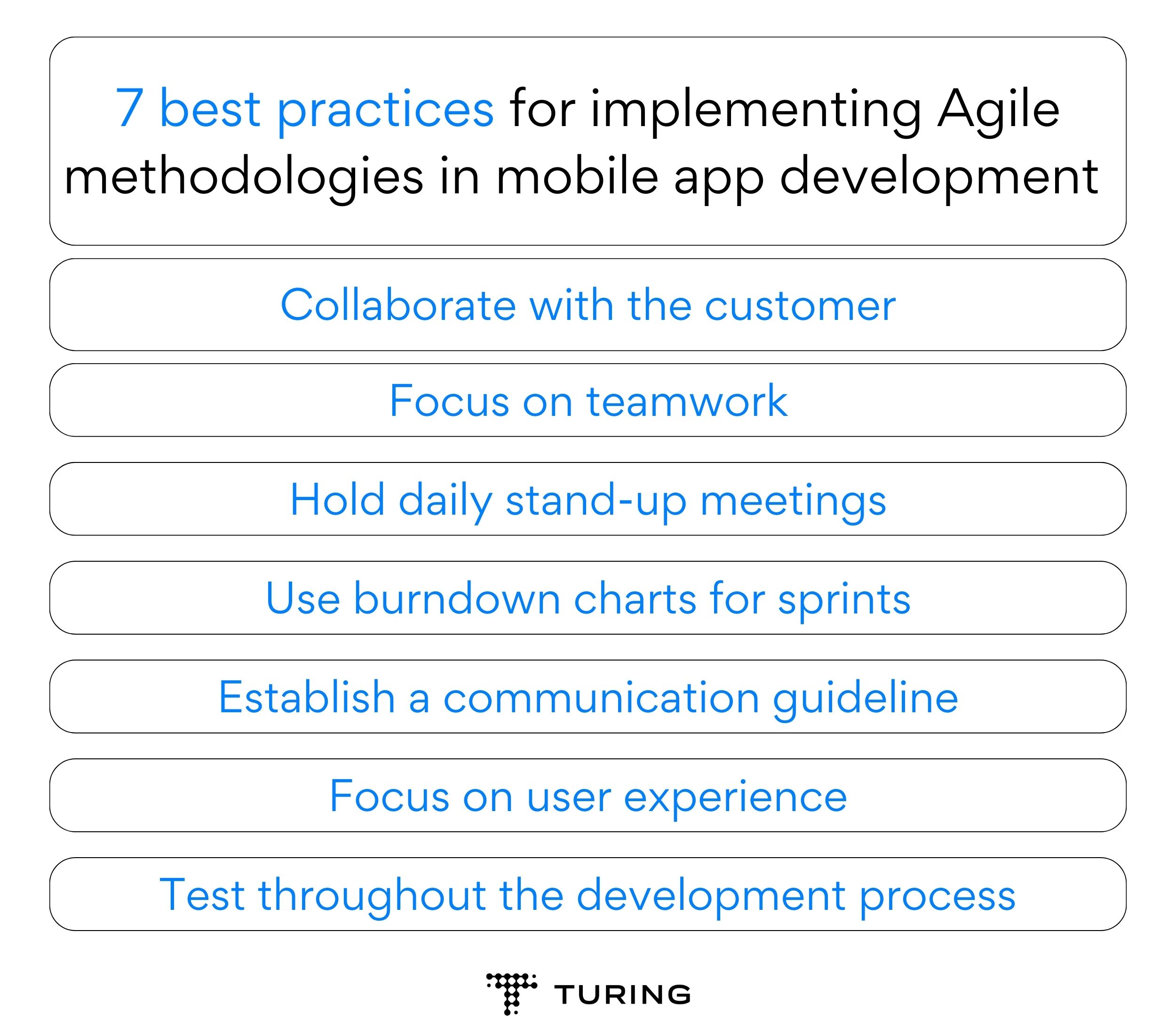
- Scrum: Scrum is a popular Agile framework, particularly suitable for complex projects with changing requirements. It segments the development cycle into fixed-length iterations called sprints, usually spanning two to four weeks. Scrum involves daily stand-up meetings, sprint planning, sprint review, and retrospective meetings, fostering transparency and continuous improvement.
- Kanban: Kanban is a visual project management framework emphasizing on flow and continuous delivery. It utilizes a Kanban board to visualize work items, workflow, and bottlenecks. As work progresses, tasks move across the board’s stages, providing real-time visibility into the project’s status. Kanban is especially beneficial for teams handling a steady stream of work with varying priorities.
- Lean: Inspired by lean manufacturing principles, Lean-Agile emphasizes the elimination of waste and the continuous delivery of value. It encourages small batch sizes, rapid feedback loops, and a customer-centric approach. Lean Agile is ideal for streamlining processes and optimizing resource utilization.
- Extreme Programming (XP): XP is an Agile framework that prioritizes technical excellence and customer satisfaction. It emphasizes practices such as test-driven development, continuous integration, and pair programming to ensure a high-quality product.
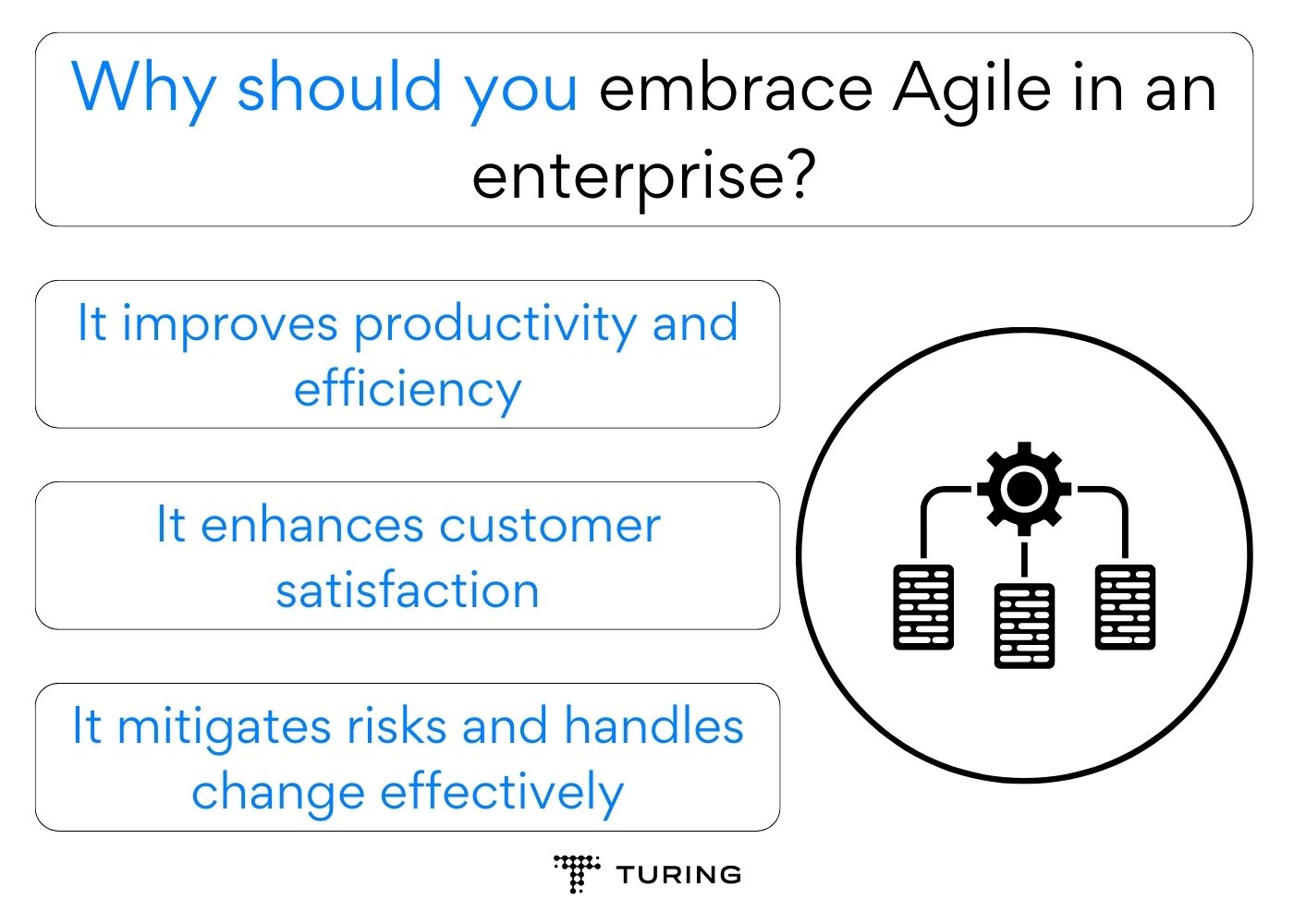
Why should you embrace Agile in an enterprise?
Why should you embrace Agile in an enterprise?
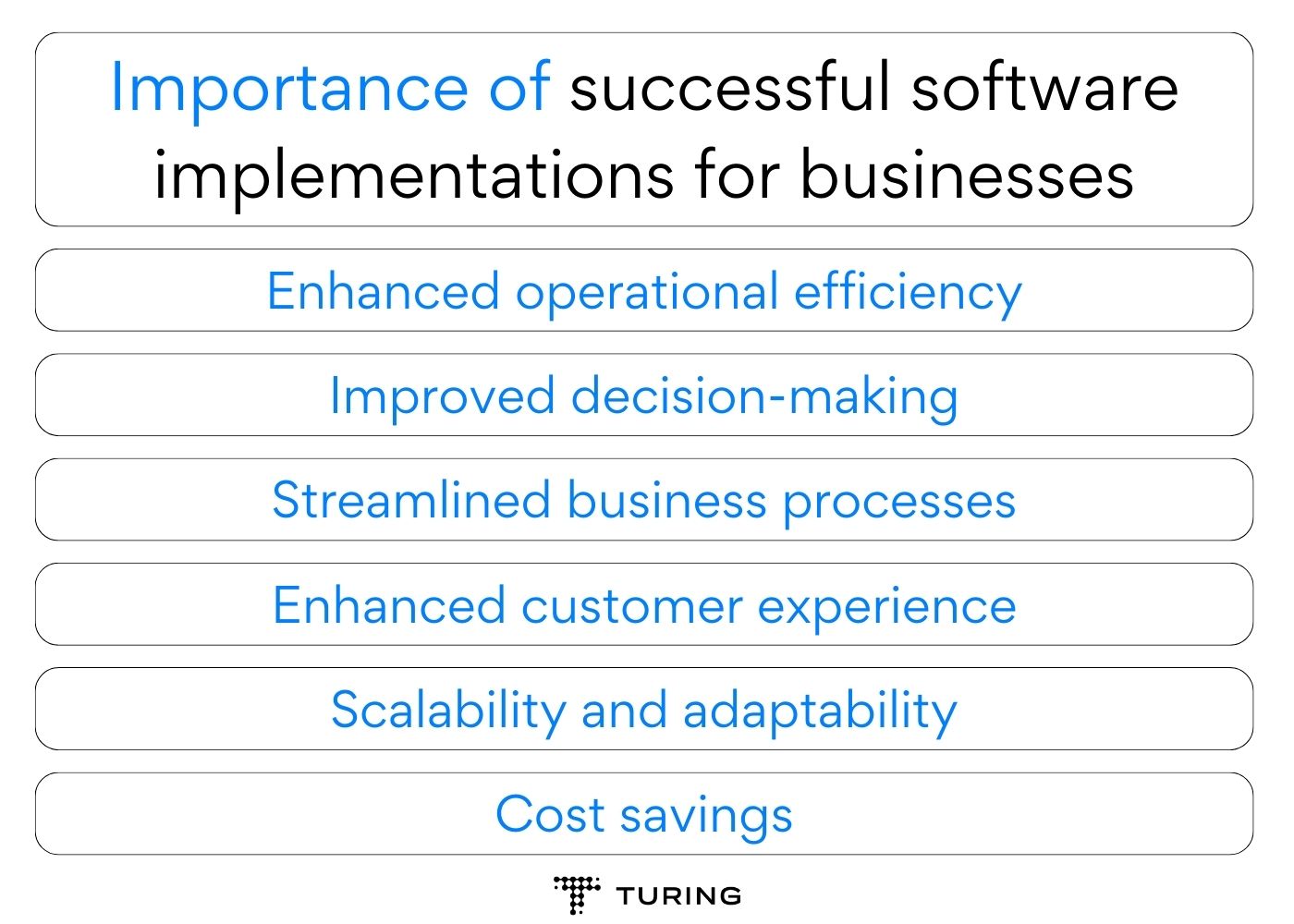
Agile methodology has emerged as a transformative approach that empowers organizations to achieve business goals. Embracing Agile in an enterprise can lead to improved productivity and efficiency, enhanced customer satisfaction, and effective risk mitigation strategies. Let’s look at some compelling reasons to adopt Agile practices and thrive in the fast-paced world of technology.
-
It improves productivity and efficiency
One of the primary reasons to adopt Agile in an enterprise is its remarkable impact on productivity and efficiency. Agile breaks down projects into manageable iterations, allowing teams to focus on delivering value incrementally. The iterative development approach enables early identification of issues and prompt resolution, minimizing time wasted on unproductive tasks.
Moreover, Agile practices, such as daily stand-up meetings and regular retrospectives, promote transparency and communication among team members. This leads to a deeper understanding of project progress and challenges, enabling teams to make data-driven decisions and optimize their processes continually.
By optimizing workflows, eliminating bottlenecks, and fostering collaboration, Agile empowers enterprises to streamline their operations and achieve higher productivity levels, ensuring projects are completed on time and within budget.
-
It enhances customer satisfaction
Customer satisfaction is a critical metric of success for any enterprise. Agile methodology places a strong emphasis on customer collaboration throughout the project lifecycle. By involving customers early on and seeking their feedback regularly, Agile teams ensure that the delivered product aligns precisely with customer expectations.
Through the incremental delivery of functional features, customers can witness tangible progress and provide feedback that shapes subsequent iterations. This iterative feedback loop results in a product that not only meets customer needs but also adapts to their evolving requirements, fostering a deeper sense of customer satisfaction and loyalty.
Incorporating customer-centricity into Agile practices helps enterprises gain a competitive advantage by delivering products that truly address the customers’ pain points and preferences.
-
It mitigates risks and handles change effectively
Modern industries are inherently filled with uncertainties and risks. Agile excels at risk mitigation by embracing change as a natural part of the development process. Rather than avoiding change, Agile teams are empowered to respond to it swiftly and effectively.
In Agile projects, risk management strategies are integrated throughout the development lifecycle. By identifying potential risks early on, teams can develop contingency plans and actively work to mitigate these risks. Frequent feedback loops ensure that risks are constantly evaluated and addressed, reducing the likelihood of major setbacks.
Furthermore, Agile’s adaptive nature allows enterprises to handle unforeseen changes, such as shifting market demands or emerging technologies, with agility and confidence. This ability to respond quickly to change positions enterprises to seize opportunities and navigate challenges with resilience.
Risk management strategies in Agile projects
Here are some key risk management strategies that Agile projects employ:
- Continuous risk identification: Agile teams hold regular meetings, such as sprint planning, daily stand-ups, and retrospectives, where potential risks are discussed and assessed. By maintaining constant vigilance, teams can detect risks early, allowing sufficient time to develop appropriate responses.
- Collaborative risk assessment: During collaborative sessions, such as sprint reviews or customer feedback meetings, risks are openly discussed and analyzed. This collective effort ensures that diverse perspectives are considered, leading to a more comprehensive understanding of risks and potential solutions.
- Risk prioritization: Not all risks have an equal impact on project outcomes. Agile teams prioritize risks based on their severity and potential consequences. High-priority risks that may significantly impact project success are addressed first, while low-priority risks are managed as the project progresses. Prioritization enables teams to allocate resources effectively and focus on mitigating the most critical risks.
- Incremental risk mitigation: Agile’s iterative approach allows for incremental risk mitigation. Instead of attempting to address all risks at once, teams focus on mitigating the most urgent risks during each iteration. This phased approach ensures that risks are actively managed as the project evolves, reducing the chances of unexpected challenges derailing the project.
What are the challenges in enterprise Agile transformation?
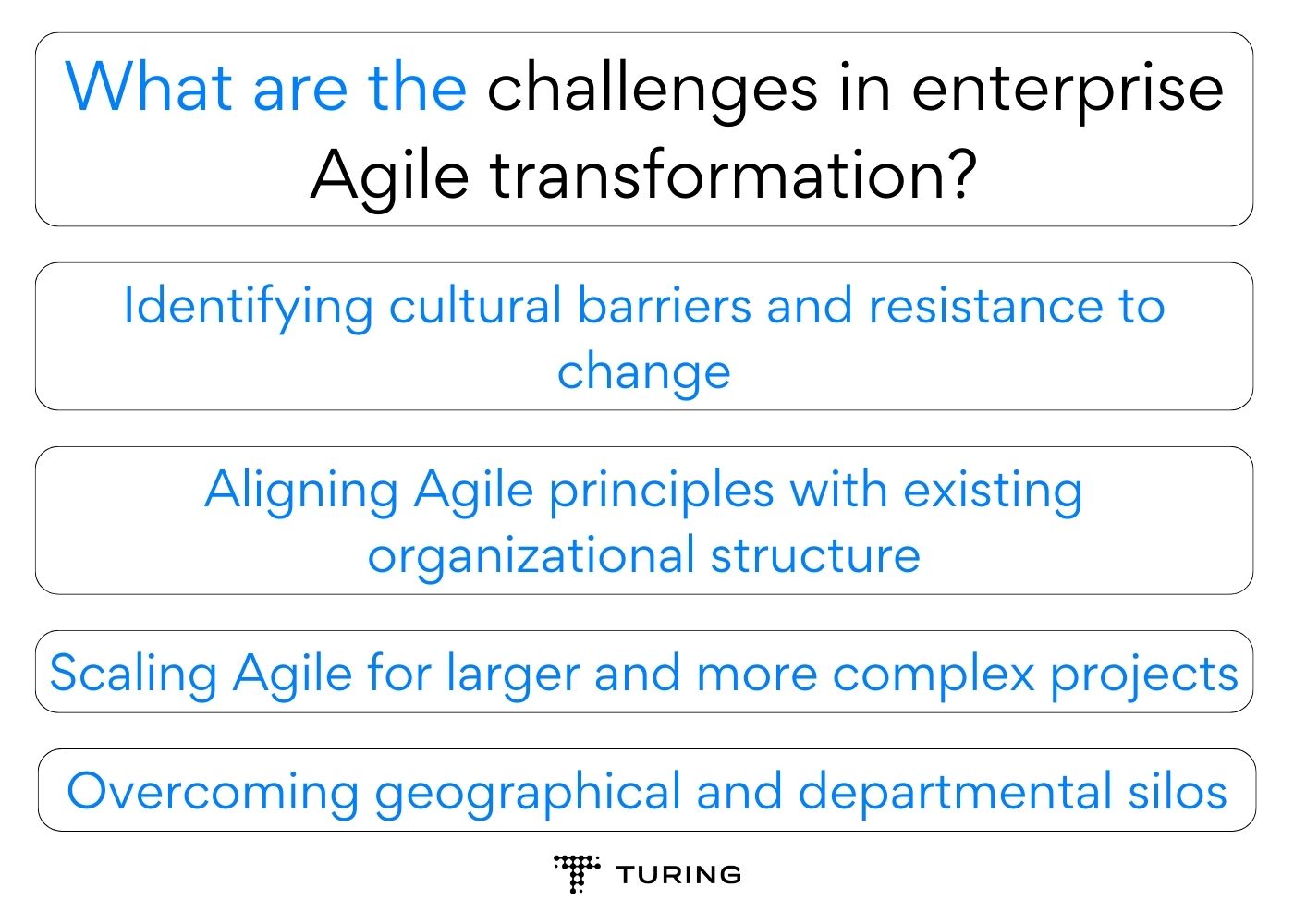
What are the challenges in enterprise Agile transformation?
For larger enterprises and established organizations, adopting Agile principles can be a complex and challenging process. This section aims to address the common hurdles faced during enterprise Agile transformation and provides insights into overcoming them for successful implementation.
-
Identifying cultural barriers and resistance to change
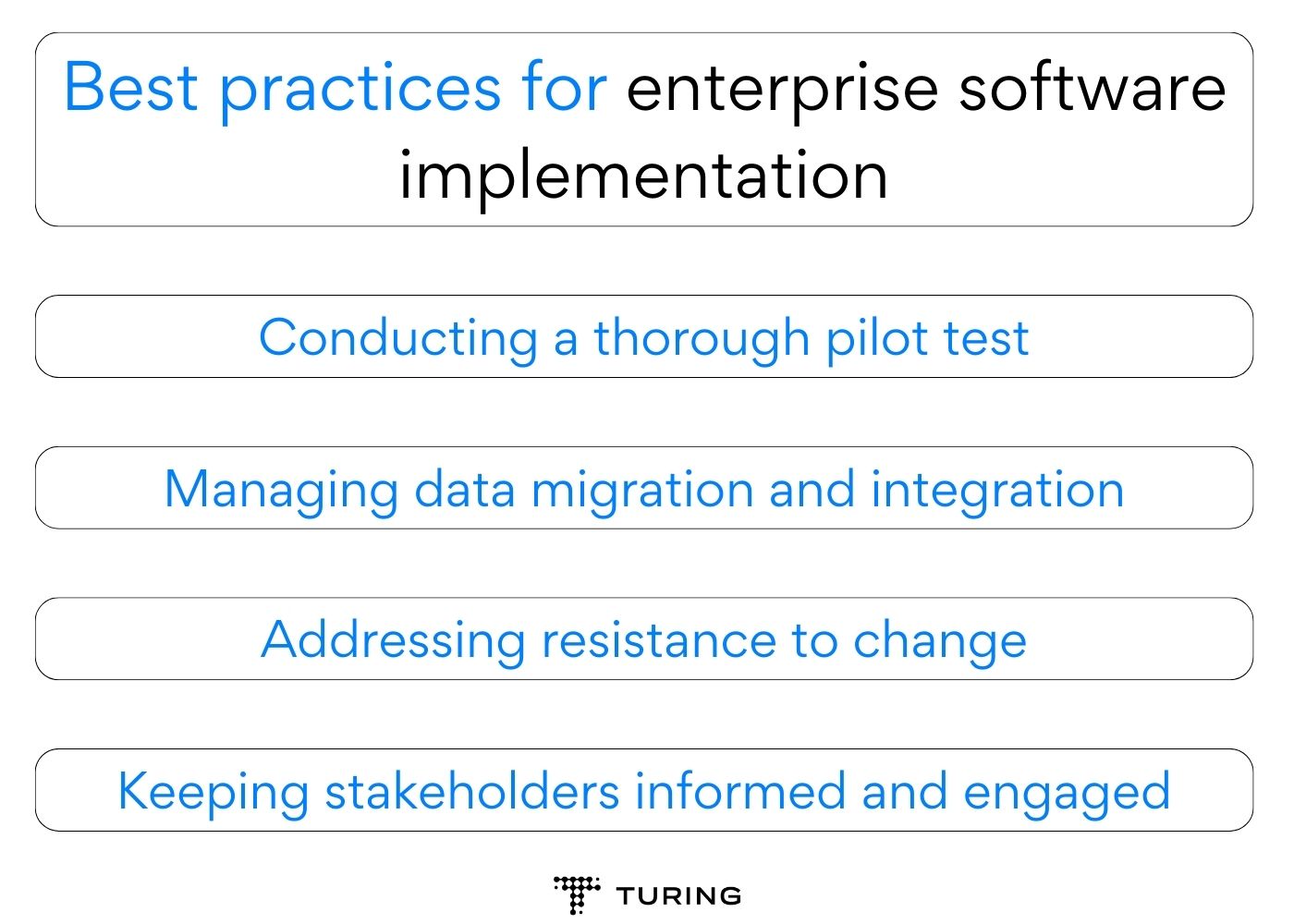
One of the primary challenges in enterprise Agile transformation is cultural resistance to change. In many organizations, traditional hierarchical structures and long-standing practices are deeply ingrained. Embracing Agile values and practices may encounter resistance from employees who fear losing control, perceived uncertainty, or a shift in power dynamics.
To overcome these cultural barriers, leaders must foster a culture of transparency, collaboration, and continuous learning. Regular communication about the benefits of Agile, its positive impact on individual roles, and the organization as a whole will help ease apprehensions.
Additionally, providing comprehensive training and mentoring programs can empower employees to embrace the Agile mindset and practices confidently.
-
Aligning Agile principles with existing organizational structure
Enterprise Agile transformation requires aligning Agile principles with an organization’s existing structure. Many enterprises have complex hierarchies and established processes that may seem incompatible with Agile’s flexible and iterative approach.
To address this challenge, companies should adopt a tailored approach to Agile implementation. Tailoring Agile practices to fit the specific needs and characteristics of the organization can enhance the chances of successful adoption.
Organizations can start with pilot projects and gradually expand Agile practices across departments, allowing teams to adapt and refine their approach as they progress.
-
Scaling Agile for larger and more complex projects
While Agile methodologies are inherently designed for flexibility and adaptability, scaling Agile to handle larger and more complex projects presents unique challenges. Traditional Agile frameworks like Scrum or Kanban may prove insufficient for large enterprise projects involving multiple teams, dependencies, and longer development cycles.
To scale Agile effectively, organizations can consider adopting Agile scaling frameworks such as SAFe (Scaled Agile Framework), LeSS (Large-Scale Scrum), or DAD (Disciplined Agile Delivery). These frameworks provide a structured approach to managing cross-team coordination, communication, and alignment, allowing enterprises to maintain Agile principles while dealing with complex project requirements.
-
Overcoming geographical and departmental silos
In globally distributed enterprises or organizations with multiple departments, geographical and departmental silos can hinder Agile transformation. Effective collaboration and communication become challenging when teams are physically separated or have different reporting structures.
To break down these silos, organizations must foster a culture of collaboration and open communication. Leveraging collaboration tools and technologies can bridge the gap between geographically dispersed teams.
Regular virtual meetings, workshops, and team-building exercises can enhance inter-departmental relationships and strengthen the collective Agile mindset across the organization.
Steps to facilitate a smooth Agile transformation
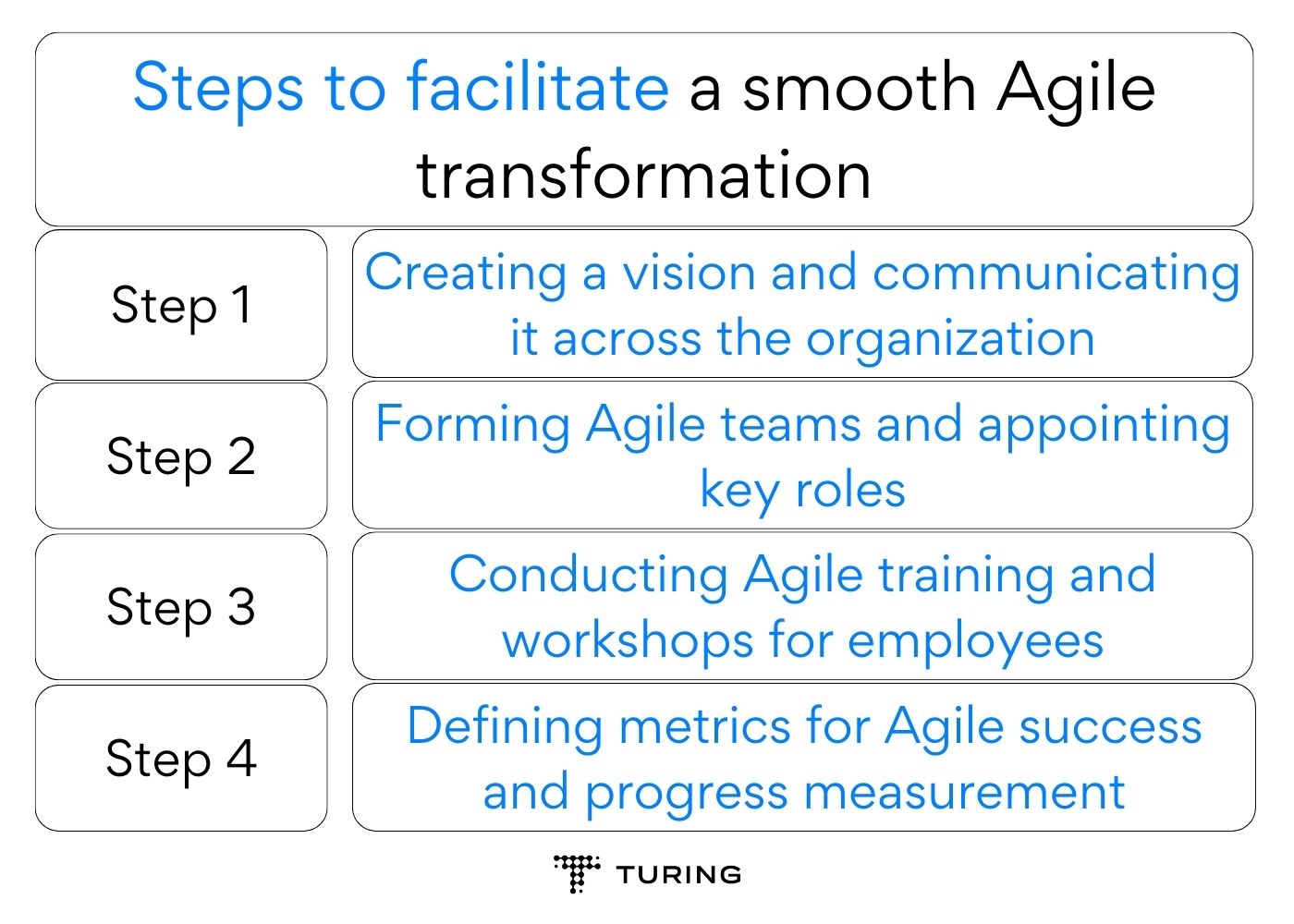
Steps to facilitate a smooth Agile transformation
From establishing a compelling vision and forming collaborative teams to providing essential training and implementing measurable success metrics, these steps will guide enterprises toward a successful Agile adoption. This adoption will ensure long-term success and growth in the ever-evolving technological landscape.
Step:1- Creating a vision and communicating it across the organization
A successful Agile transformation begins with a clear vision and a shared understanding of why the change is necessary. Enterprises should define their Agile goals, expected outcomes, and how it aligns with the company’s overall strategic objectives. Communicating this vision across all levels of the organization is vital to gain buy-in and support from stakeholders and employees.
Leadership plays a crucial role in communicating the vision. Executives and managers should articulate the benefits of Agile, emphasizing how it fosters innovation, increases customer satisfaction, and enhances organizational adaptability. Regular town-hall meetings, emails, and internal presentations can help reinforce the message and create a sense of purpose among employees.
Step:2- Forming Agile teams and appointing key roles
A fundamental aspect of Agile transformation is forming cross-functional and self-organizing Agile teams. These teams will be the backbone of Agile implementation, responsible for delivering value to customers and driving continuous improvement. Assembling teams with diverse skill sets and expertise ensures better problem-solving and collaboration.
To enable seamless Agile implementation, key roles such as Scrum Masters and Product Owners should be appointed carefully. Scrum Masters act as facilitators, guiding teams in Agile practices and removing impediments.
Product owners, on the other hand, represent the customer’s interests, prioritize the product backlog, and ensure the team delivers maximum value.
Step:3- Conducting Agile training and workshops for employees
Transitioning to Agile requires a change in mindset and a shift in how work is planned and executed. Agile training and workshops are instrumental in equipping employees with the necessary knowledge and skills to embrace the Agile way of working.
Comprehensive Agile training should cater to employees at all levels, from top management to individual contributors. Training sessions can cover various Agile frameworks, principles, and best practices. Hands-on workshops and simulations can help employees grasp Agile concepts better and apply them to real-world scenarios.
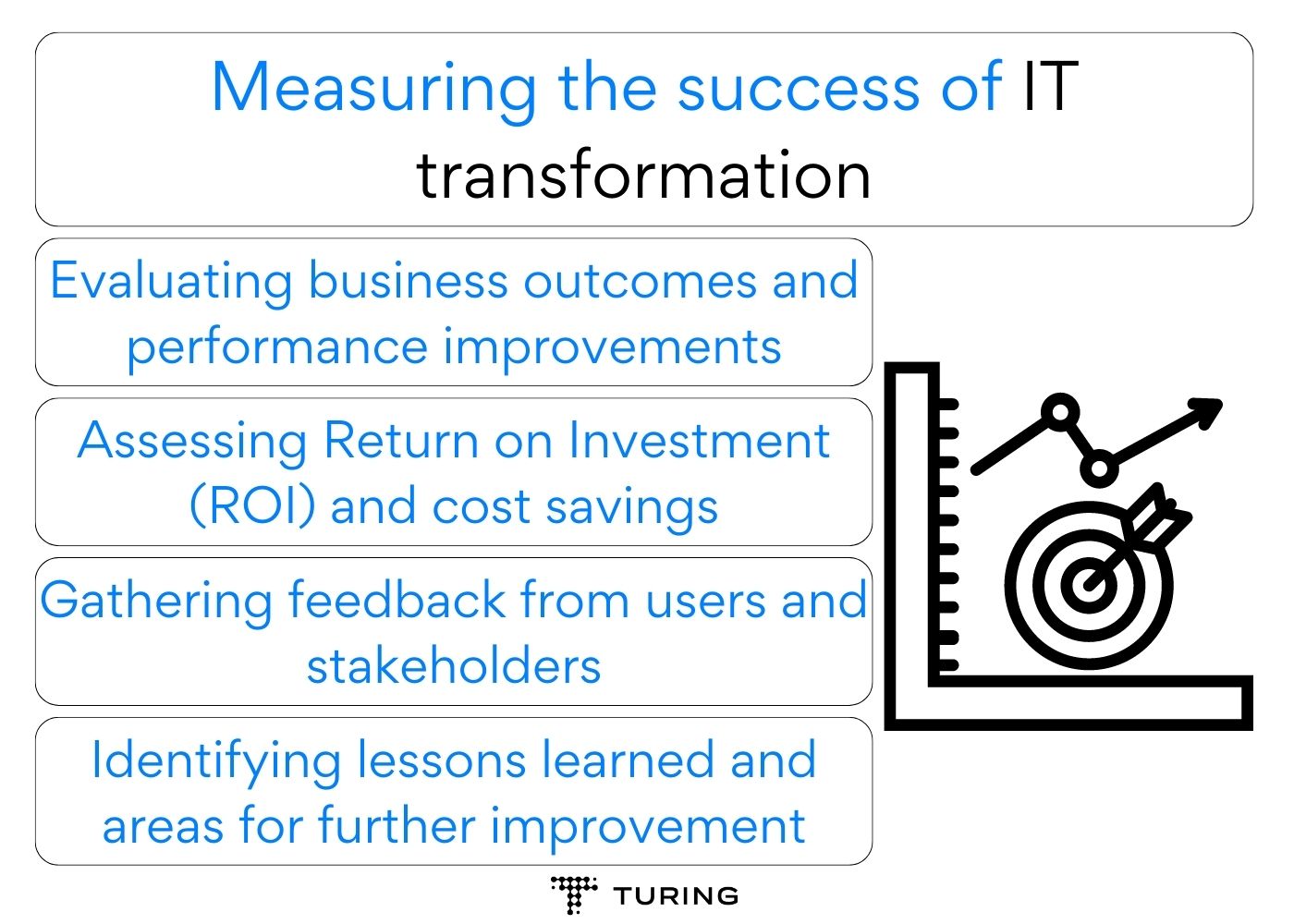
Step:4- Defining metrics for Agile success and progress measurement
Measuring the success of Agile transformation is crucial to track progress and identify areas for improvement. Enterprises should define relevant metrics aligned with their Agile goals and regularly monitor them throughout the transformation journey.
Common Agile metrics include velocity, lead time, cycle time, customer satisfaction, and team productivity. These metrics provide valuable insights into the effectiveness of Agile practices, project health, and customer-centricity. Regular reviews and retrospectives allow teams to adapt their approach and continuously enhance their Agile implementation.
Choosing the right Agile framework for enterprise transformation
As enterprises embark on their Agile transformation journey, selecting the most suitable framework becomes crucial for success. Here are some essential considerations when choosing the right Agile framework for enterprise transformation.
-
Evaluating the specific needs and objectives of the organization
Every organization has unique characteristics, processes, and goals. Before selecting an Agile framework, it is vital to thoroughly evaluate the specific needs and objectives of the enterprise. Engage stakeholders from different departments and levels to gain a comprehensive understanding of the challenges and opportunities that Agile aims to address.
Consider factors such as the size of the organization, existing project management practices, team distribution (local or global), and the nature of projects typically undertaken. Understanding these aspects will help identify the areas where Agile can bring the most significant benefits and influence the choice of the appropriate framework.
-
Understanding the differences between Scrum, Kanban, and other frameworks
The Agile landscape offers several popular frameworks, each with its own unique characteristics and benefits. Among them, Scrum and Kanban are the most widely adopted. Understanding the fundamental differences between these frameworks is essential to make an informed decision:
- Scrum: Scrum is a time-boxed, iterative framework that divides work into fixed-length sprints, typically two to four weeks long. It prescribes specific roles (Scrum Master, Product Owner, and Development Team) and ceremonies (Daily Standup, Sprint Planning, Review, and Retrospective) to guide the development process. Scrum provides a structured approach to managing projects and fosters collaboration and accountability.
- Kanban: Kanban, on the other hand, is a flow-based framework that visualizes the workflow on a Kanban board, allowing teams to manage work items as they progress from one stage to another. It emphasizes continuous delivery, limiting work in progress, and improving overall flow efficiency. Kanban provides flexibility and is ideal for organizations with unpredictable workloads or service-oriented projects.
Apart from Scrum and Kanban, other frameworks like Lean, XP (Extreme Programming), and SAFe (Scaled Agile Framework) may be suitable for specific enterprise contexts. Research and explore these frameworks thoroughly to determine which one aligns best with the organization’s objectives and work culture.
-
Tailoring Agile processes to fit the organization’s context
Once an Agile framework is chosen, it is essential to tailor its implementation to fit the unique context of the organization. Attempting a one-size-fits-all approach may lead to resistance and hinder the Agile transformation.
Involve key stakeholders and Agile experts to identify the modifications needed to align the chosen framework with the organization’s existing processes and culture. Customize roles, ceremonies, and artifacts to suit the organization’s context while staying true to the core Agile principles.
Moreover, consider conducting pilot projects to test the effectiveness of the tailored Agile processes before scaling them across the entire organization. Iterative feedback and improvement are crucial for refining the Agile implementation and optimizing its impact.
Measuring success and continuous improvement
To ensure the success of Agile adoption, enterprises must establish clear metrics and key performance indicators (KPIs) to measure progress and facilitate continuous improvement. Let’s explore the importance of defining KPIs for Agile transformation, monitoring and analyzing Agile metrics, and implementing feedback loops to drive iterative improvements.
-
Defining KPIs (Key Performance Indicators) for Agile transformation
KPIs are vital for gauging the effectiveness of Agile transformation and its alignment with organizational goals. Defining the right KPIs enables enterprises to track progress, identify bottlenecks, and ensure that Agile practices lead to positive outcomes. Some essential KPIs for Agile transformation include:
- Cycle time: Cycle time measures the time taken to complete a task or project from initiation to delivery. A shorter cycle time indicates improved efficiency and faster time-to-market.
- Velocity: Velocity measures the amount of work completed by an Agile team in a single iteration (sprint). Consistently increasing velocity signifies team productivity and capacity for delivering value.
- Customer satisfaction: Regularly obtaining feedback from customers and stakeholders helps assess their satisfaction levels. Higher customer satisfaction reflects the successful adoption of Agile practices to meet customer needs.
- Employee engagement: Monitoring employee engagement levels throughout the transformation ensures that Agile practices positively impact the workforce, fostering a culture of collaboration and ownership.
- Agile maturity: Assessing the level of Agile maturity across teams and departments provides insights into the overall transformation progress.
Defining these KPIs early in the Agile transformation process sets a clear direction and ensures that efforts align with business objectives.
-
Monitoring and analyzing Agile metrics
Once KPIs are established, enterprises must diligently monitor and analyze relevant Agile metrics to derive actionable insights. Agile metrics offer real-time visibility into project performance, allowing teams to make data-driven decisions and adapt their approach accordingly.
Regularly reviewing burn-down charts, cumulative flow diagrams, and lead-time distribution charts helps teams identify potential roadblocks, bottlenecks, and areas for improvement. This data-driven approach enables Agile teams to optimize processes and enhance productivity throughout the transformation journey.
-
Implementing feedback loops and iterative improvements
Continuous improvement is at the heart of Agile methodologies. Enterprises should encourage a culture of feedback and learning to foster innovation and growth. Implementing feedback loops allows teams to reflect on their performance, gather insights from stakeholders, and identify opportunities for refinement.
Regular retrospectives are a vital feedback mechanism for Agile teams. These meetings provide a safe space for team members to openly discuss what went well and what could be improved during the iteration. The insights gained from retrospectives can lead to iterative improvements that drive efficiency and quality over time.
Additionally, organizations can leverage Agile maturity assessments to identify areas that require further attention and investment. These assessments help in understanding the level of Agile adoption, highlighting both strengths and areas for growth, and guiding the next steps in the transformation journey.
Common pitfalls to avoid during Agile transformation
Embarking on an Agile transformation journey brings its own challenges. To ensure a successful transition, enterprises must be aware of common pitfalls that can hinder the process. Here are three critical pitfalls to avoid during Agile transformation.
-
Going “Agile” in name only (Agile in theory, Waterfall in practice)
One of the most significant pitfalls in Agile transformation is falling into the trap of being “Agile” in name only. This phenomenon, often referred to as “Agile in theory, Waterfall in practice,” occurs when organizations claim to be Agile but continue to follow traditional, linear project management practices behind the scenes.
This lack of genuine commitment to Agile principles can lead to confusion, frustration, and suboptimal results. To avoid this pitfall, enterprises need to embrace Agile values and practices wholeheartedly. Teams must prioritize iterative development, continuous feedback, and collaboration, breaking free from rigid hierarchies and siloed departments.
Only by fully immersing themselves in the Agile mindset can organizations harness the true potential of Agile transformation.
-
Ignoring the importance of continuous learning and adaptation
Agile methodologies thrive on a culture of continuous learning and adaptation. Unfortunately, some enterprises overlook this crucial aspect, assuming that adopting Agile frameworks is a one-time effort. In reality, Agile transformation is an ongoing journey that requires constant reflection, learning, and adaptability.
Neglecting the continuous improvement mindset can lead to stagnation and missed growth opportunities. Agile teams should regularly conduct retrospectives to review their processes, celebrate successes, and identify areas for enhancement.
Moreover, organizations should encourage experimentation and risk-taking, allowing teams to learn from failures and pivot as needed.
-
Neglecting the role of leadership in Agile transformation
Leadership plays a pivotal role in shaping the success of Agile transformation. Without strong support and active involvement from top management, Agile initiatives may face significant roadblocks. Leaders must champion the Agile transformation, demonstrate commitment to Agile values, and lead by example.
When leadership neglects Agile principles or reverts to traditional command-and-control styles, it creates a disconnect between the vision and the implementation. This can lead to resistance from employees and hinder the Agile transformation process.
To avoid this pitfall, leadership should provide the necessary resources, training, and guidance for teams to embrace Agile methodologies. Leaders must foster a culture of trust, empowerment, and open communication, enabling teams to take ownership and deliver value to customers effectively.
Conclusion
In conclusion, the transition from traditional methodologies to Agile is a transformative journey that holds immense potential for enterprises across industries. By overcoming common pitfalls, such as going “Agile” in name only and neglecting continuous learning, organizations can unlock the true power of Agile transformation.
Embracing a culture of collaboration, adaptability, and continuous improvement will pave the way for success in today’s dynamic business landscape. As enterprises wholeheartedly embrace Agile with strong leadership support, they experience sustainable growth and enhanced customer satisfaction, gaining a competitive edge along the way.
Turing’s enterprise app services provide invaluable assistance to enterprises in their Agile transformation journey. Our experts bring extensive knowledge of Agile methodologies and software development, enabling organizations to implement Agile practices effectively. With our support, enterprises can enhance collaboration, responsiveness, and overall productivity, ensuring a successful Agile transformation.
Tell us the skills you need and we'll find the best developer for you in days, not weeks.
Hire Developers